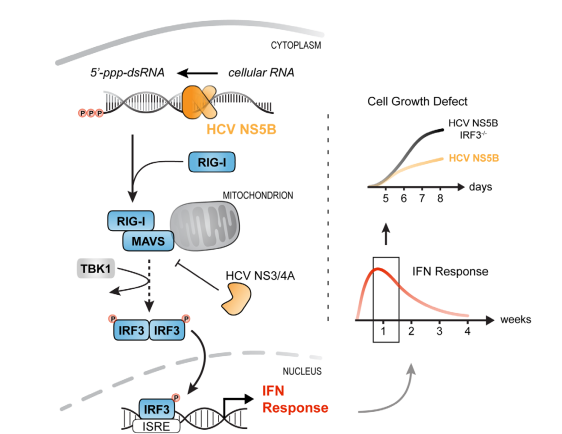
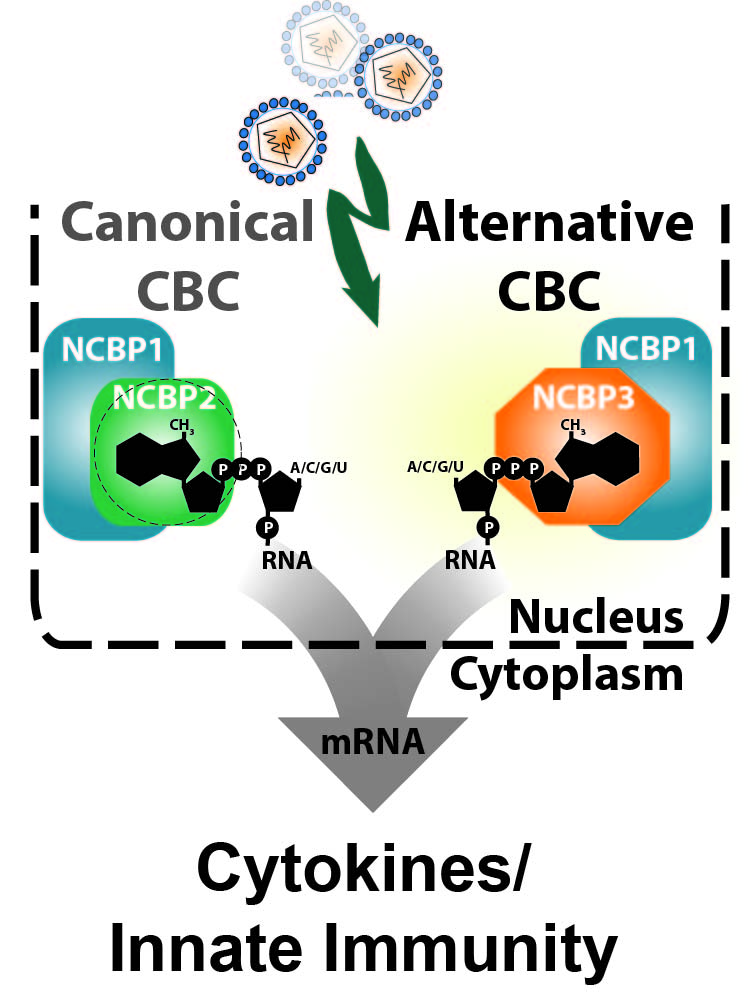
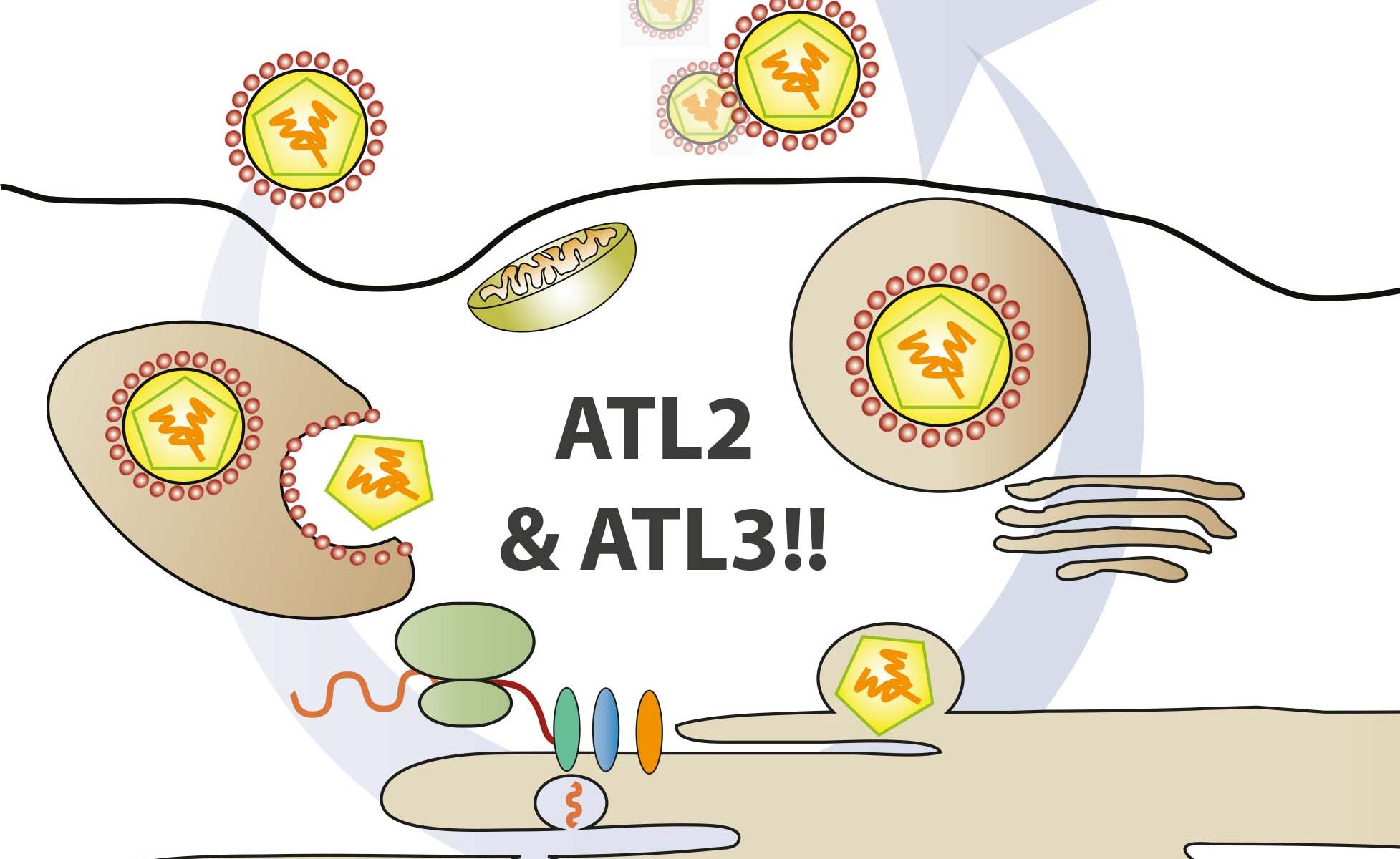
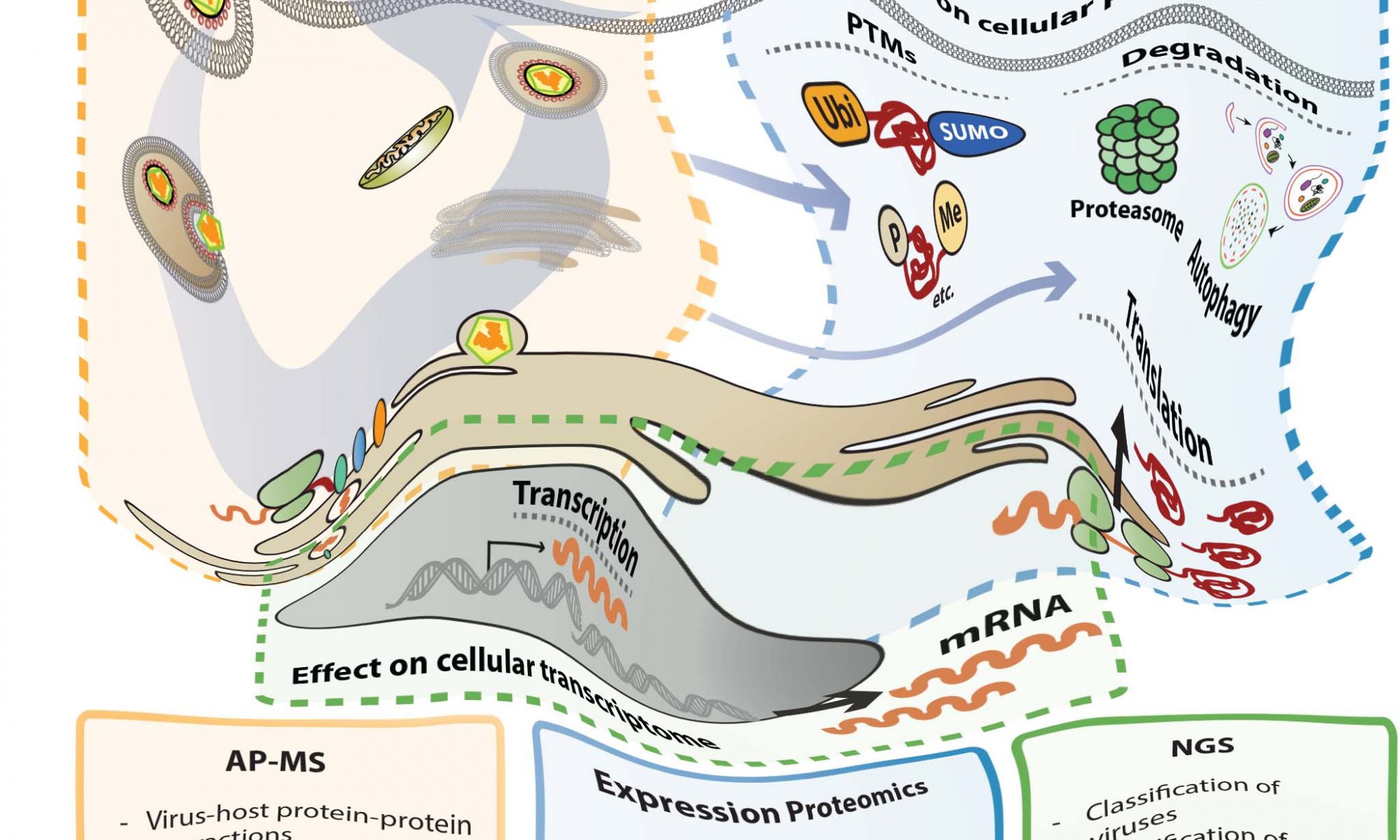
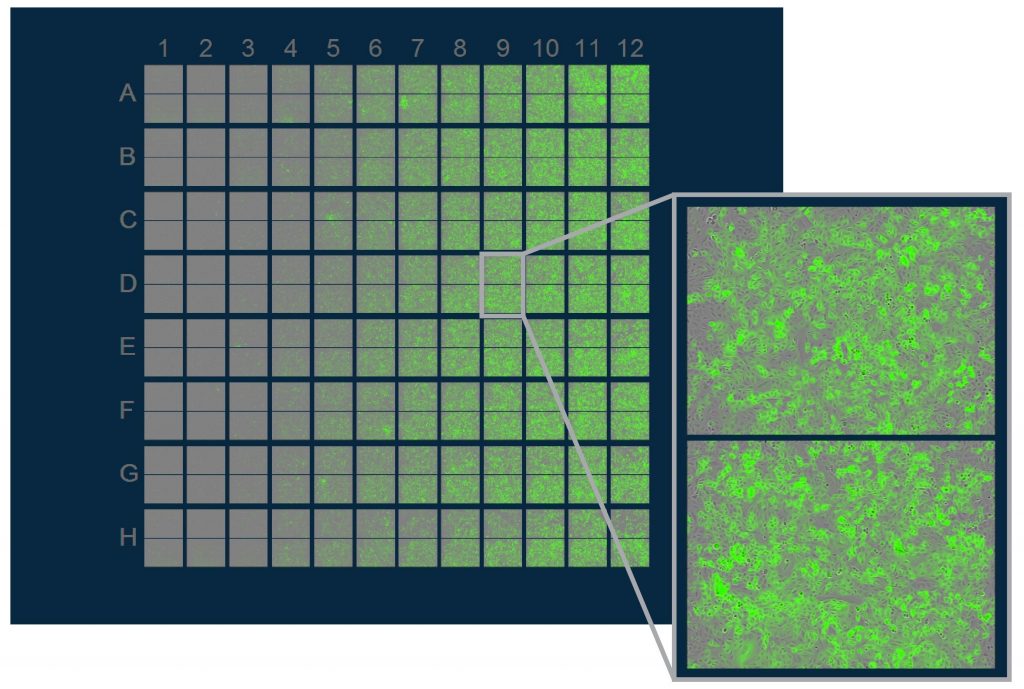
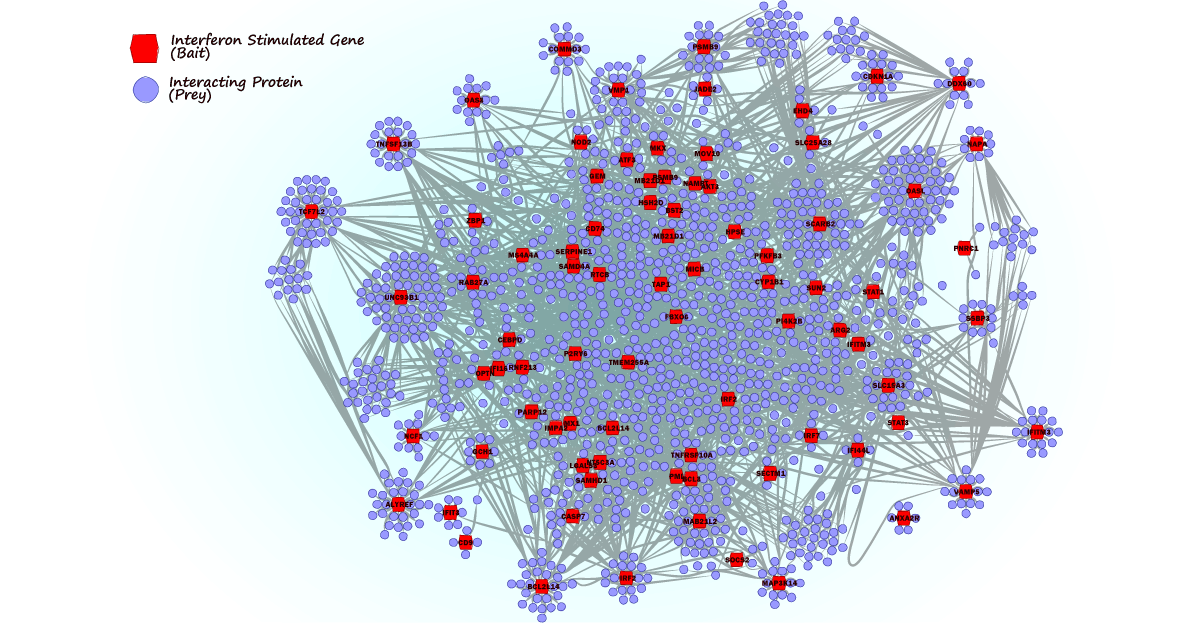
In this collaborative project, Chris and Hendrik found that long-term delivery of RIG-I ligand leads to cytostasis. Surprisingly, unlike found for other innate immune stimuli (e.g. LPS) persistent activation of the RIG-I pathway does not lead to tolerance. We hypothesize that this system recapitulates the situation in HCV-infected livers, which requires constant re-infection of cells in order to persistently propagate the virus. A beautiful story – which you can read here.