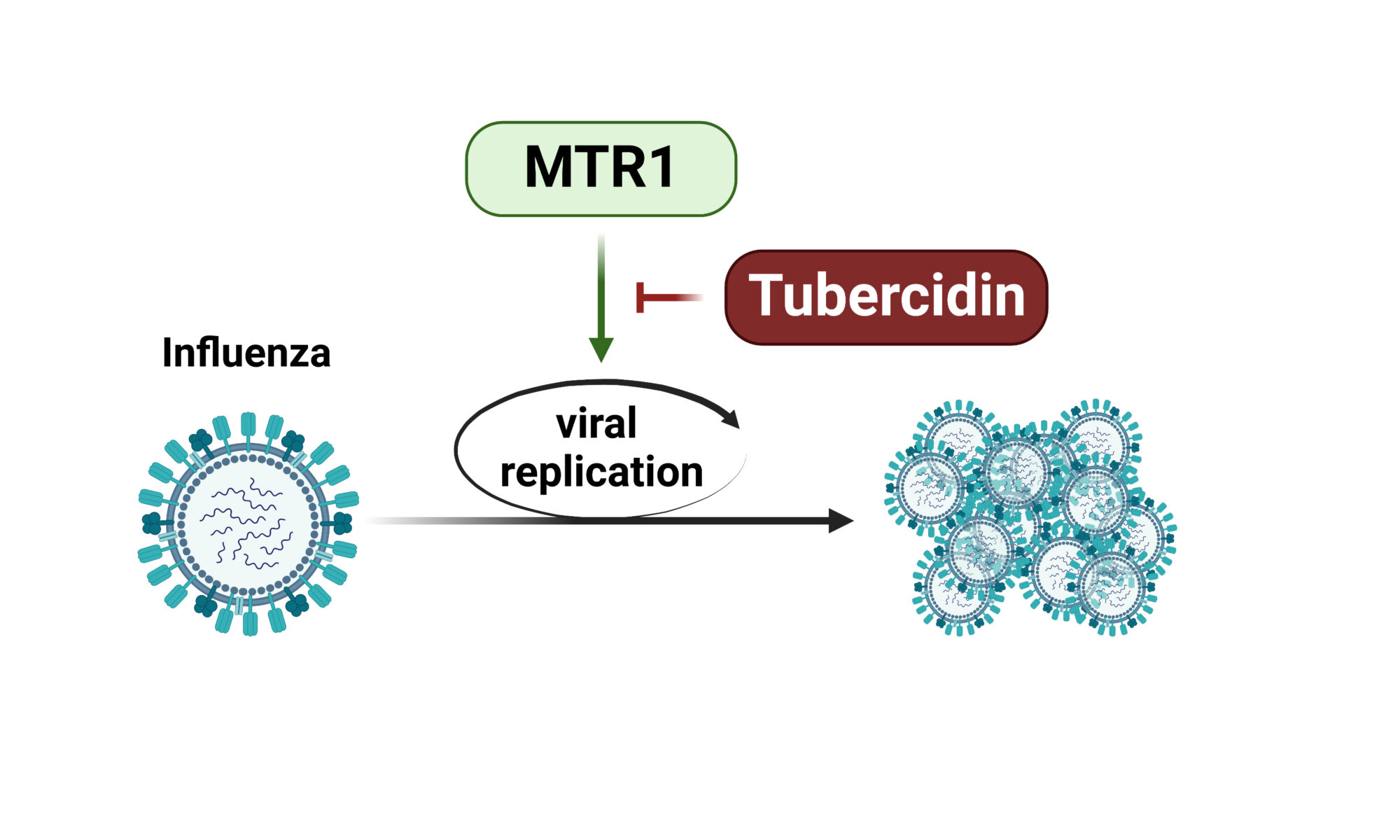
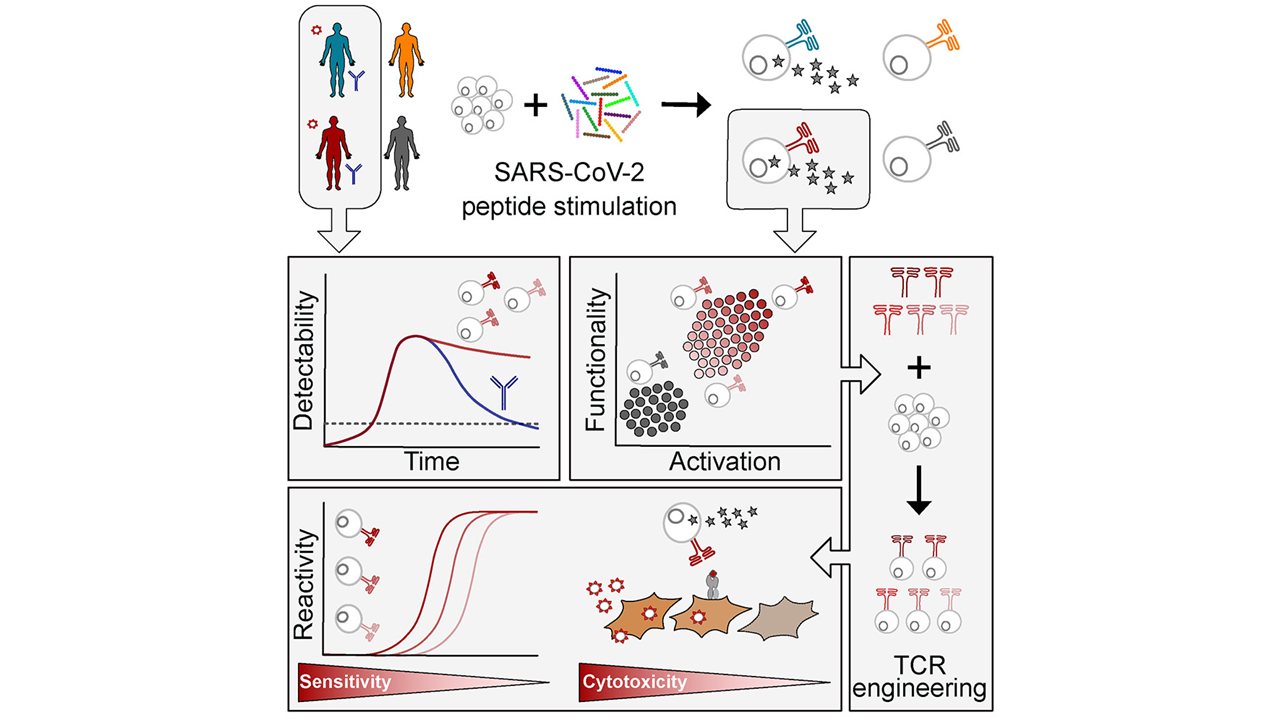
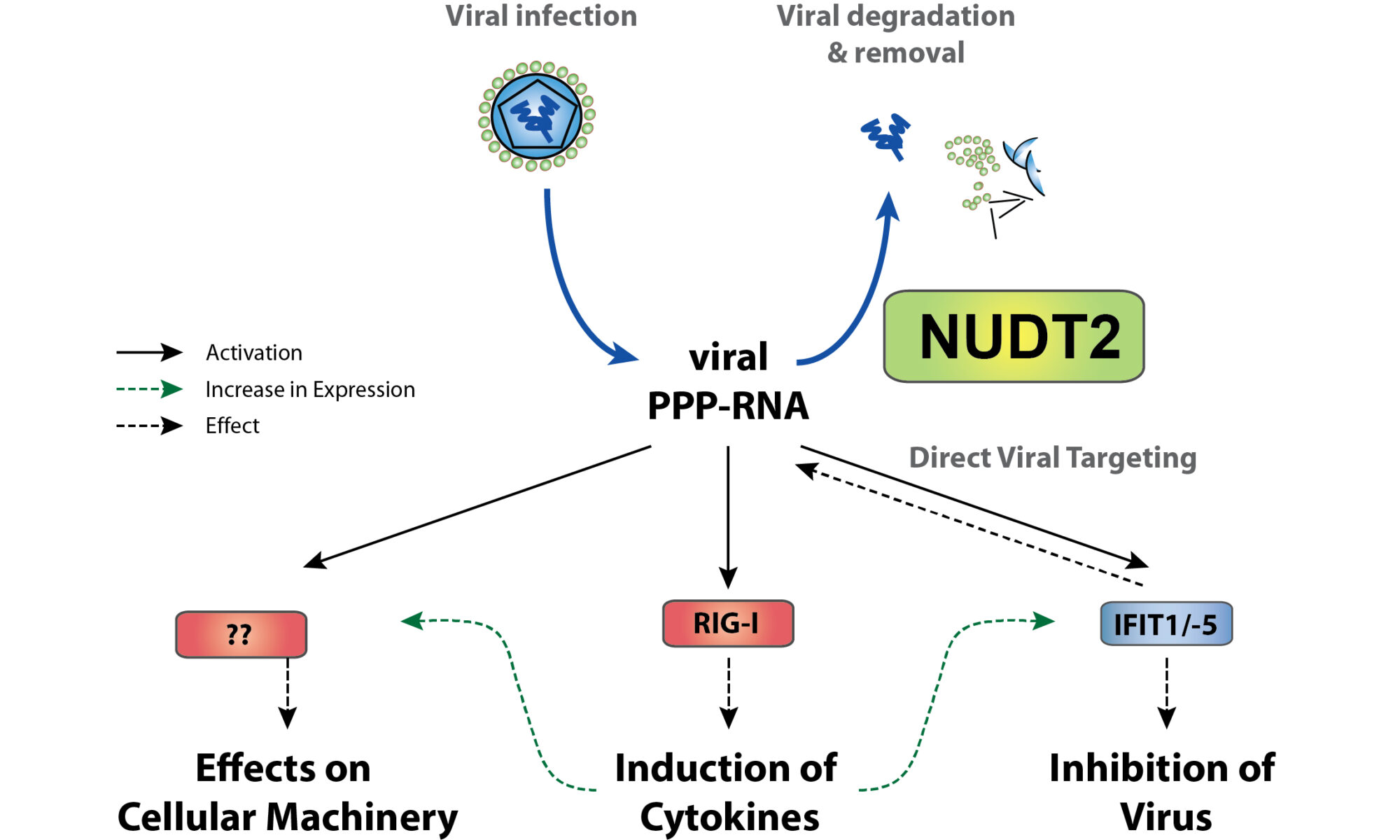
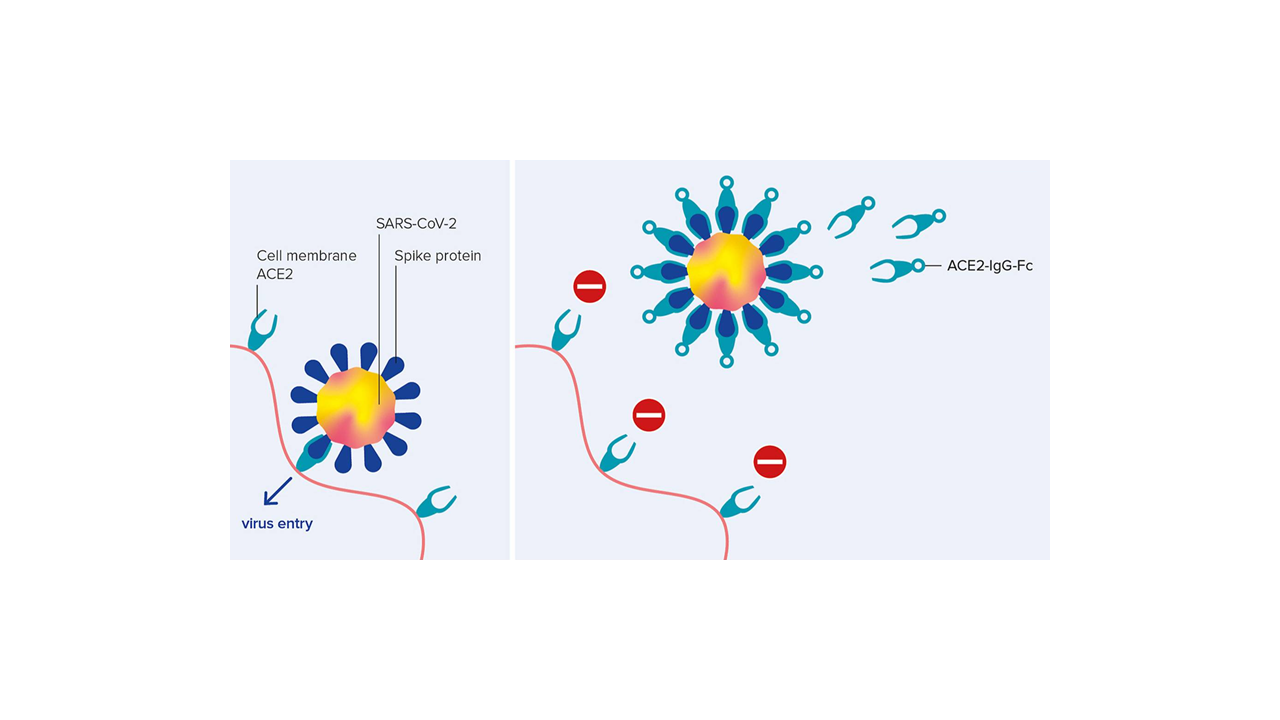
We are proud to be part of the massive effort, spearheaded by Hiroki Kato and his team from Bonn, that revealed the critical role of the host RNA 2’O-methyltransferase MTr1 in influenza A/B cap-snatching! The activity of MTr1 is pivotal for Influenza A and B but not for other cap-snatching viruses and can be inhibited by a host-directed small molecule to achieve an antiviral effect through a novel mechanism.
Congratulations to Hiroki Kato in Bonn and collaborators for the fabulous manuscript published in Science!
Read more here: Inhibition of cellular RNA methyltransferase abrogates influenza virus capping and replication
Text by Valter and illustration by Andreas.